What follows is the text of my presentation, Functional options for friendly APIs
that I gave at dotGo this year. It has been edited slightly for readability.
I want to thank Kelsey Hightower, Bill Kennedy, Jeremy Saenz, and Brian Ketelsen, for their assistance in preparing this talk.

I want to begin my talk with a story.
It is late 2014, your company is launching a revolutionary new distributed social network. Wisely, your team has chosen Go as the language for this product.
You have been tasked with writing the crucial server component. Possibly it looks a little like this.
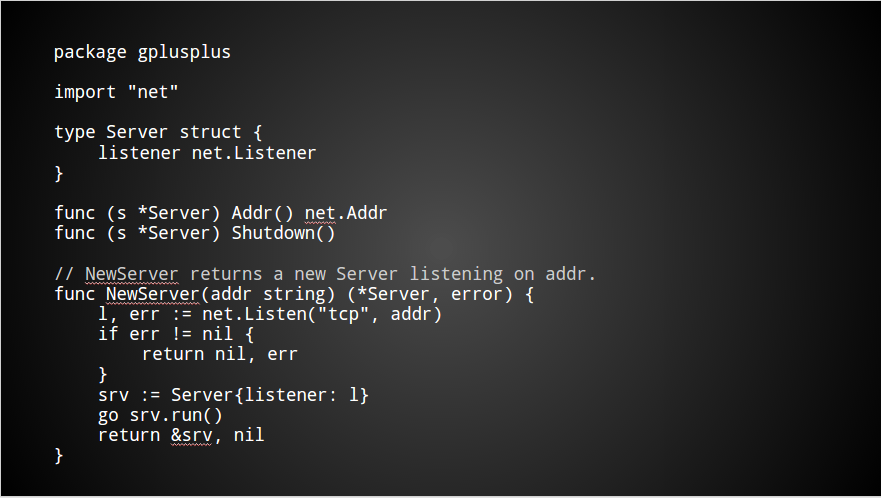
There are some unexported fields that need to be initialised, and a goroutine must be started to service incoming requests.
The package has a simple API, it is pretty easy to use.
But, there is a problem. Soon after you announce your first beta release, the feature requests start to roll in.

Mobile clients are often slow to respond, or stop responding altogether—you’ll need to add support for disconnecting these slow clients.
In this climate of heightened security awareness, your bug tracker starts to fill with demands to support secure connections.
Then, you get a report from a user who is running your server on a very small VPS. They need a way to limit the number of simultaneous clients.
Next is the request to rate limit concurrent connections from a group of users being targeted by a botnet.
… and on it goes.
Now, you need to change your API to incorporate all these feature requests.

It’s kind of a sign that things are not going well when the function won’t easily fit on a slide.
Show of hands, who has used an API like this ?
Who has written an API like this ?
Who has had their code break while depending on an API like this ?
Obviously this solution is cumbersome and brittle. It also isn’t very discoverable.
Newcomers to your package have no idea which parameters are optional, and which are mandatory.
For example, if I want to create an instance of the Server for testing, do I need to provide a real TLS certificate ? If not, what do I provide instead ?
If I don’t care about maxconns, or maxconcurrent what value should I use ? Do I use zero ? Zero sounds reasonable, but depending on how the feature was implemented, that might limit you to zero total concurrent connections.
It appears to me, that writing an API like this can be easy; as long as you make it the caller’s responsibility to use it correctly.
While this example could be a considered an exaggeration, maliciously constructed and compounded by poor documentation, I believe that it demonstrates a real issue with ornate, brittle APIs such as this.
So now that I’ve defined the problem, lets look at some solutions.

Rather than trying to provide one single function which must cater for every permutation, a solution might be to create a set of functions.
With this approach, when callers need a secure server they can call the TLS variant.
When they need to establish a maximum duration for idle connections, they can use the variant that takes a timeout.
Unfortunately, as you can see, providing every possible permutation can quickly become overwhelming.
Let’s move on to others way of making your API configurable.
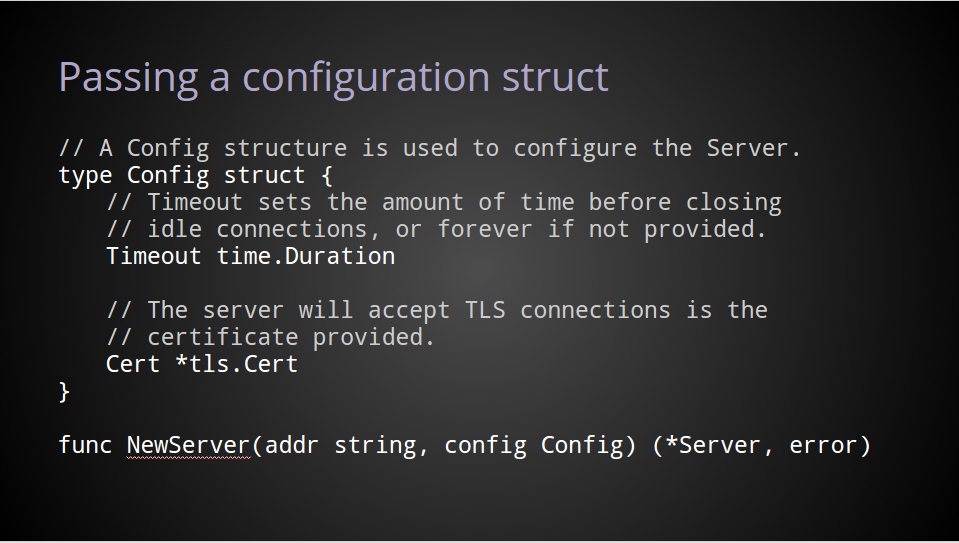
A very common solution is to use a configuration struct.
This has some advantages.
Using this approach, the configuration struct can grow over time as new options are added, while the public API for creating a server itself remains unchanged.
This method can lead to better documentation.
What was once a massive comment block on the NewServer function, becomes a nicely documented struct.
Potentially it also enables the callers to use the zero value to signify they they want the default behaviour for a particular configuration option.
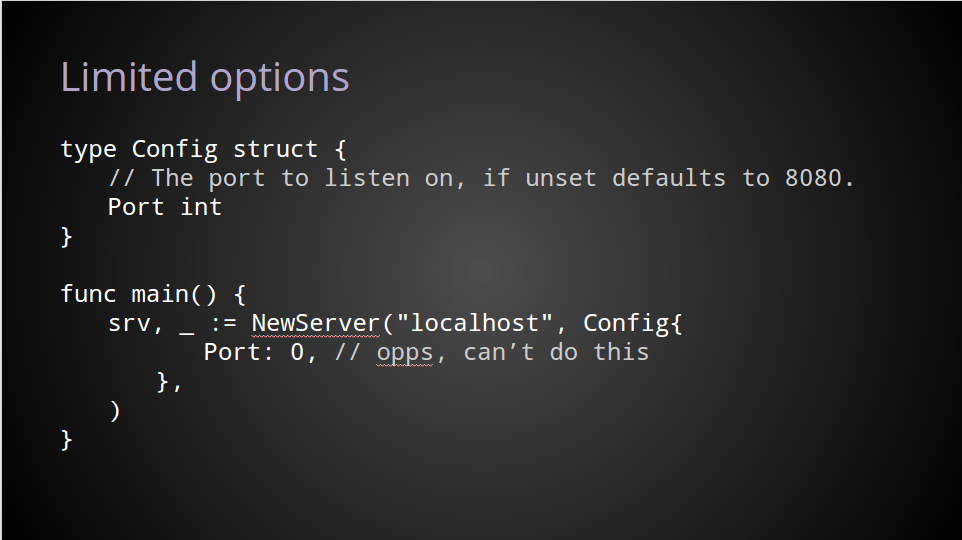
However, this pattern is not perfect.
It has trouble with defaults, especially if the zero value has a well understood meaning.
For example, in the config structure shown here, when Port is not provided, NewServer will return a *Server for listening on port 8080.
But this has the downside that you can no longer explicitly set Port to 0 and have the operating system automatically choose a free port, because that explicit 0 is indistinguishable from the fields’ zero value.

Most of the time, users of your API will be expecting to use its default behaviour.
Even though they do not intend to change any of the configuration parameters, those callers are still required to pass something for that second argument.
So, when people read your tests or your example code, trying to figure out how to use your package, they’ll see this magic empty value, and it’ll become enshrined in the collective unconsciousness.
[and] to me, this just feel wrong.
Why should users of your API be required to construct an empty value, simply to satisfy the signature of the function ?
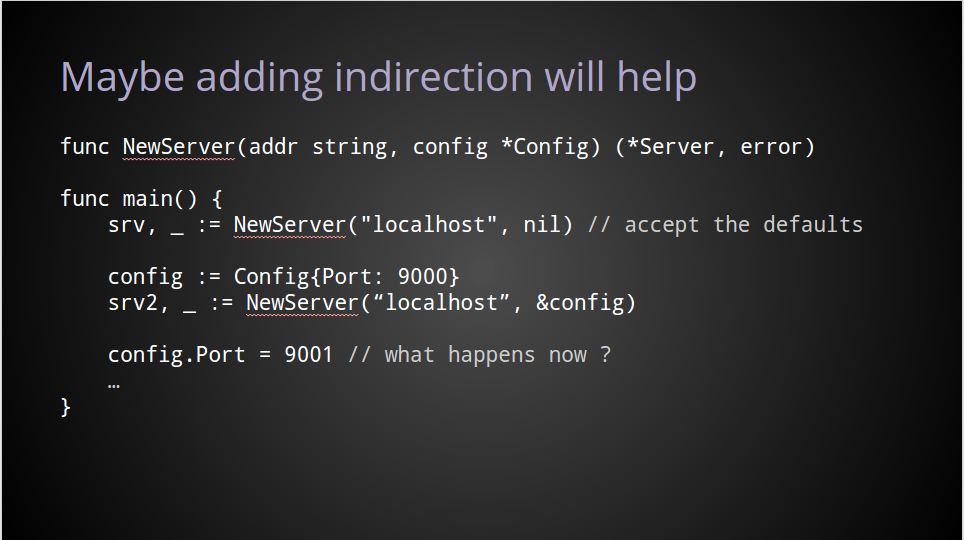
A common solution to this empty value problem is to pass a pointer to the value instead, thereby enabling callers to use nil rather than constructing an empty value.
In my opinion this pattern has all the problems of the previous example, and it adds a few more.
We still have to pass something for this function’s second argument, but now this value could be nil, and most of the time will be nil for those wanting the default behaviour.
It raises the question, is there a difference between passing nil, and passing a pointer to an empty value ?
More concerning to both the package’s author, and its callers, is the Server and the caller can now share a reference to the same configuration value. Which gives rise to questions of what happens if this value is mutated after being passed to the NewServer function ?
I believe that well written APIs should not require callers to create dummy values to satisfy those rarer use cases.
I believe that we, as Go programmers, should work hard to ensure that nil is never a parameter that needs to be passed to any public function.
And when we do want to pass configuration information, it should be as self explanatory and as expressive as possible.
So now with these points in mind, I want to talk about what I believe are some better solutions.
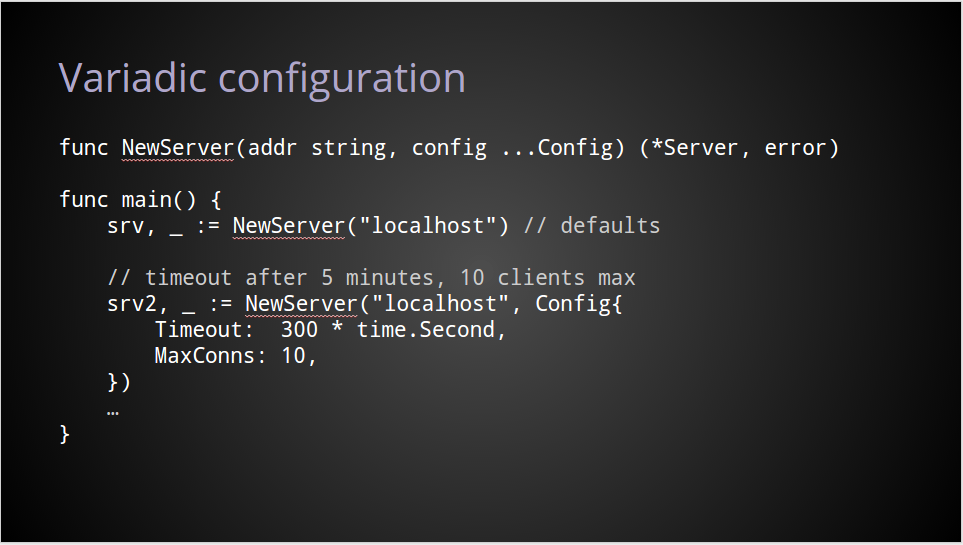
To remove the problem of that mandatory, yet frequently unused, configuration value, we can change the NewServer function to accept a variable number of arguments.
Instead of passing nil, or some zero value, as a signal that you want the defaults, the variadic nature of the function means you don’t need to pass anything at all.
And in my book this solves two big problems.
First, the invocation for the default behaviour becomes as concise as possible.
Secondly, NewServer now only accepts Config values, not pointers to config values, removing nil as a possible argument, and ensuring that the caller cannot retain a reference to the server’s internal configuration.
I think this is a big improvement.
But if we’re being pedantic, it still has a few problems.
Obviously the expectation is for you to provide at most one Config value. But as the function signature is variadic, the implementation has to be written to cope with a caller passing multiple, possibly contradictory, configuration structs.
Is there a way to use a variadic function signature and improve the expressiveness of configuration parameters when needed ?
I think that there is.
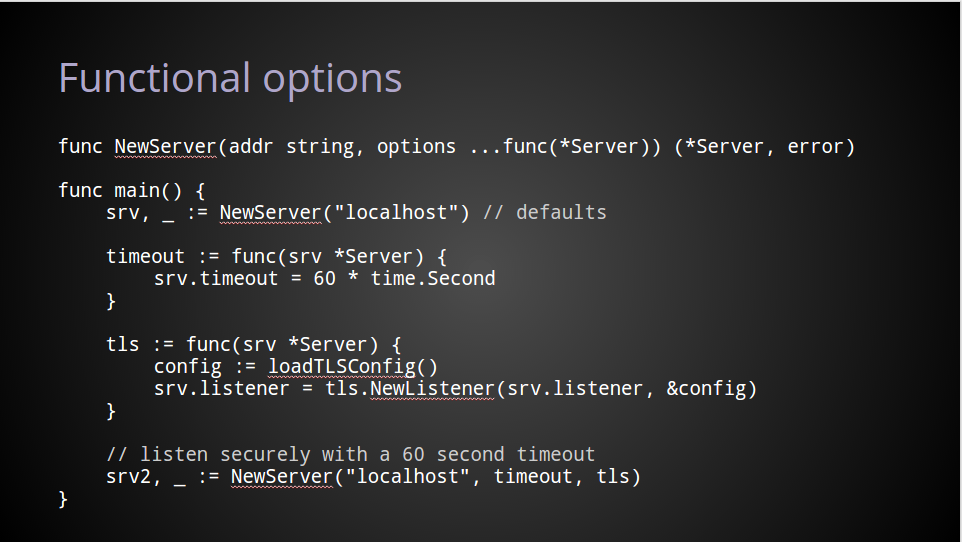
At this point I want to make it clear that that the idea of functional options
comes from a blog post titled. Self referential functions and design
by Rob Pike, published in January this year. I encourage everyone here to read it.
The key difference from the previous example, and in fact all the examples so far, is customisation of the Server is performed not with configuration parameters stored in a structure, but with functions which operate on the Server value itself.
As before, the variadic nature of the function’s signature gives us the compact behaviour for the default case.
When configuration is required, I pass to NewServer functions which operate on the Server value as an argument.
The timeout function simply changes the timeout field of any *Server value passed to it.
The tls function is a little more complicated. It takes a *Server value and wraps the original listener value inside a tls.Listener, thereby transforming it into a secure listener.
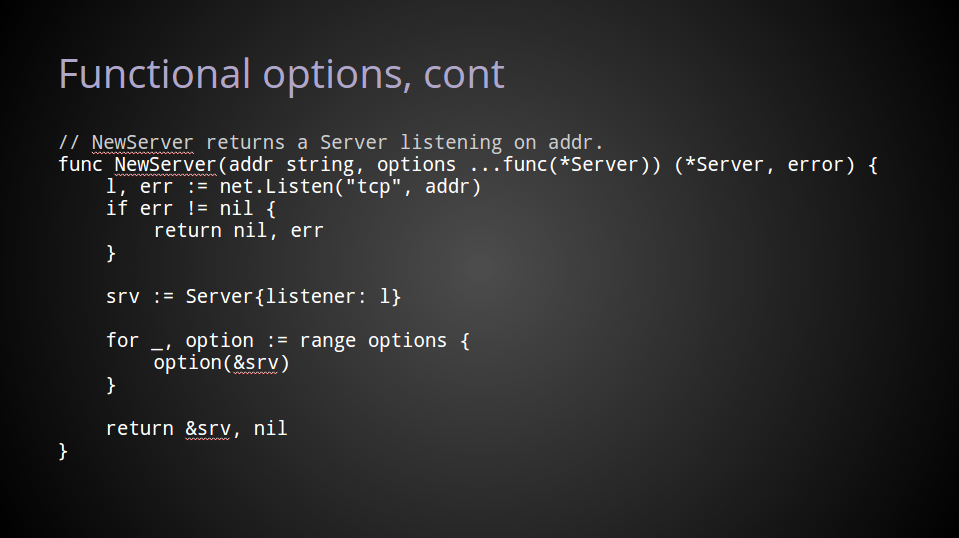
Inside NewServer, applying these options is straightforward.
After opening a net.Listener, we declare a Server instance using that listener.
Then, for each option function provided to NewServer, we call that function, passing in a pointer to the Server value that was just declared.
Obviously, if no option functions were provided, there is no work to do in this loop and so srv is unchanged.
And that’s all there is too it.
Using this pattern we can make an API that has
- sensible defaults
- is highly configurable
- can grow over time
- self documenting
- safe for newcomers
- and never requires nil or an empty value to keep the compiler happy
In the few minutes I have remaining I’d like to show you how I improved one of my own packages by converting it to use functional options.
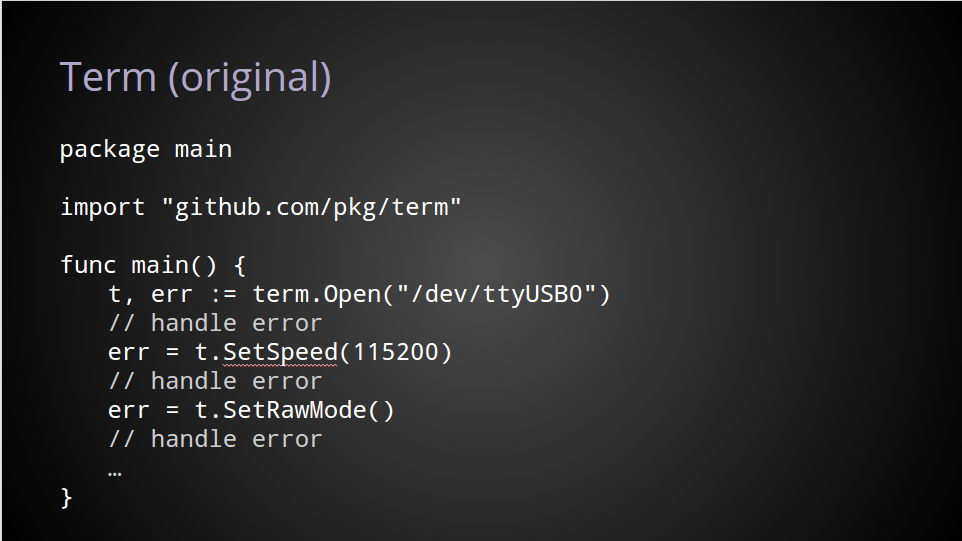
I’m an amateur hardware hacker, and many of the devices I work with use a USB serial interface. A so a few months ago I wrote a terminal handling package.
In the prior version of this package, to open a serial device, change the speed and set the terminal to raw mode, you’d have to do each of these steps individually, checking the error at every stage.
Even though this package is trying to provide a friendlier interface on an even lower level interface, it still left too many procedural warts for the user.
Let’s take a look at the package after applying the functional options pattern.
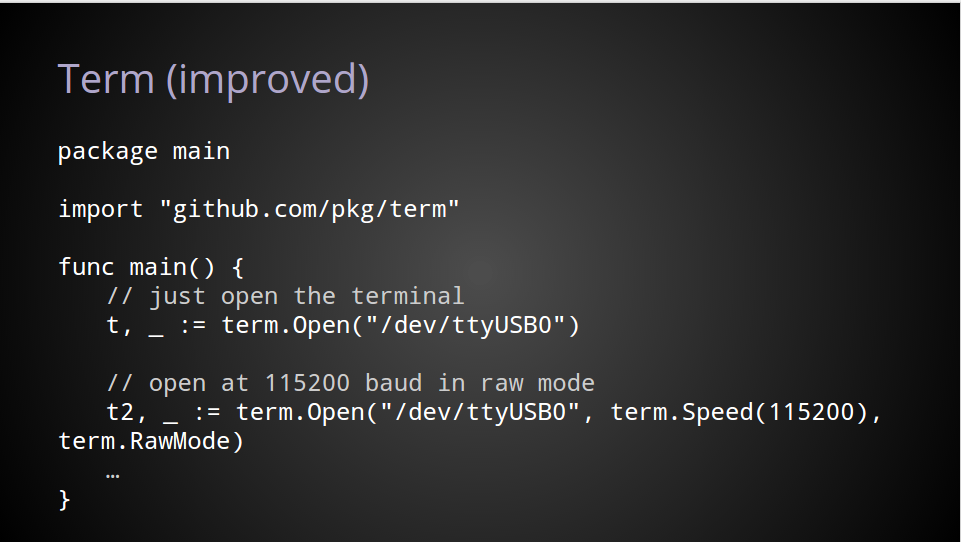
By converting the Open function to use a variadic parameter of function values, we get a much cleaner API.
In fact, it’s not just the Open API that improves, the grind of setting an option, checking an error, setting the next option, checking the error, that is gone as well.
The default case, still just takes one argument, the name of the device.
For more complicated use cases, configuration functions, defined in the term package, are passed to the Open function and are applied in order before returning.
This is the same pattern we saw in the previous example, the only thing that is different is rather than being anonymous, these are public functions. In all other respects their operation is identical.
We’ll take a look at how Speed, RawMode, and Open, are implemented on the next slide.
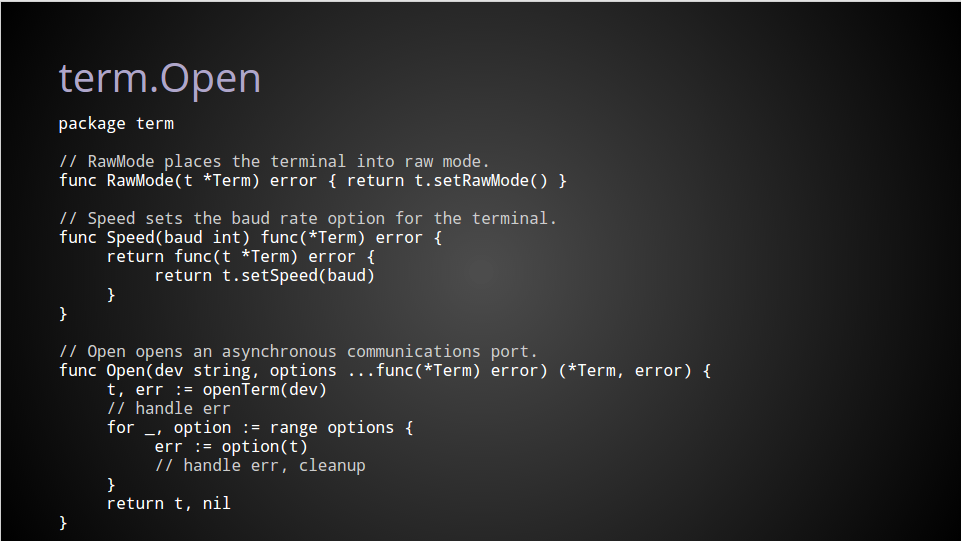
RawMode is the easiest to explain. It just a function whose signature is compatible with Open.
Because RawMode is declared in the same package as Term, it can access the private fields and call private methods declared on the Term type, in this case calling the private setRawMode helper.
Speed is also just a regular function, however it does not match the signature Open requires. This is because Speed itself requires an argument; the baud rate.
Speed returns an anonymous function which is compatible with the Open function’s signature, which closes over the baud rate parameter, capturing it for later when the function is applied.
Inside the call to Open, we first open the terminal device with the openTerm helper.
Next, just as before, we range over the slice of options functions, calling each one in turn passing in t, the pointer to our term.Term value.
If there is an error applying any function then we stop at that point, clean up and return the error to the caller.
Otherwise, returning from the function, we’ve now created and configured a Term value to the caller’s specifications.

In summary
- Functional options let you write APIs that can grow over time.
- They enable the default use case to be the simplest.
- They provide meaningful configuration parameters.
- Finally they give you access to the entire power of the language to initialize complex values.
In this talk, I have presented many of the existing configuration patterns, those considered idiomatic and commonly in use today, and at every stage asked questions like:
- Can this be made simpler ?
- Is that parameter necessary ?
- Does the signature of this function make it easy for it to be used safely ?
- Does the API contain traps or confusing misdirection that will frustrate ?
I hope I have inspired you to do the same. To revisit code that you have written in the past and pose yourself these same questions and thereby improve it.

Thank you.